How to price a product: A guide for small businesses

Interested in joining the world's leading print on demand platform?
Launching your own business is a big deal. As you’ve probably already discovered, there are a lot of decisions to make in the process — from finding your niche and developing your brand identity to building your website and pricing your products.
And since you clicked on this blog post, we’re going to go ahead and assume that you’re a small business owner trying to work out how to price your products. If our assumptions are correct, then you’ve come to the right place. Keep scrolling for our step-by-step guide on how to price a product.
Pricing your products
Selling your products for the right price is key. Too cheap and you run the risk of throwing away your profits and giving customers the impression your products are of poor quality; too expensive and you’ll scare them off altogether and lose out to businesses with more competitive prices.
The following steps pertain to a pricing strategy known as ‘cost-plus pricing’, which is a method commonly used by small businesses due to its simplicity and effectiveness. According to Wikipedia, cost-plus pricing is a technique through which “the selling price of a product is determined by adding a specific fixed percentage (a "markup") to the product's unit cost”. In other words, it enables you to establish the minimum amount you need to charge your customers in order to cover your costs and still make a profit. To use the cost-plus pricing strategy for your own business, simply follow these three easy steps:
1. Do your research
It goes without saying that you want your business to make as much money as possible, but you have to be realistic and consider how much the average shopper is willing to pay for your products. This is where market research comes in, which involves snooping on your closest competitors to find out how much they’re charging their customers (aka your potential customers). And while it might seem like a good idea to simply match their prices and call it a day, it’s not advisable unless you know exactly what their running costs are as well as the quality of the product they’re offering. For these reasons, it’s best to use the findings from your market research as more of a guide than a rule of thumb.

2. Calculate your costs
Now that you have a better understanding of how much cash your future customers are prepared to part with, it’s time to analyse your own spending habits. By calculating both your variable costs (costs that vary depending on production output) and fixed costs (costs that remain the same regardless of production output), you’ll be able to determine exactly how much you need to sell your products for in order to break even. And don’t worry if maths isn’t your strong suit, because these formulas are pretty straightforward:
Variable costs + fixed costs = cost of goods sold
Cost of goods sold ÷ number of units = break-even price per unit
Examples of potential costs for ecommerce businesses:
Variable costs
- Raw materials
- Packaging
- Shipping
- Marketing
Fixed costs
- Web-hosting fees
- Business insurance
- Internet access
- Ecommerce platform subscription fees
One of the great things about print on demand is that there are no start-up costs and typically little to no operating costs, since Prodigi takes care of everything from printing and packing your orders to dropshipping them direct to your customers. Even better, we buy and hold all of your inventory for you, so you don’t have to worry about replenishing stock or losing money through excess stock. Getting started is easy, too — all you need to launch or scale your print on demand store is an internet connection and a laptop! Sign up now, and start selling print on demand products around the world today.
3. Add a markup
Time for the exciting part: paying yourself a profit. This part of the cost-pricing strategy involves adding a markup percentage to the cost price of your products, in turn generating your gross profit. Remember that market research we talked about earlier? That’ll come in handy when it comes to working out how much markup to add. Markup percentages tend to vary depending on the type of products you’re selling but, generally speaking, they can range anywhere from 20% to 50%. And the higher your markup, the bigger your profit. Put into practice, you should end up with something that looks a little something like this:
sale price
$2.50
gross profit
33.33%
gross margin
(gross profit as a percentage of the selling price)
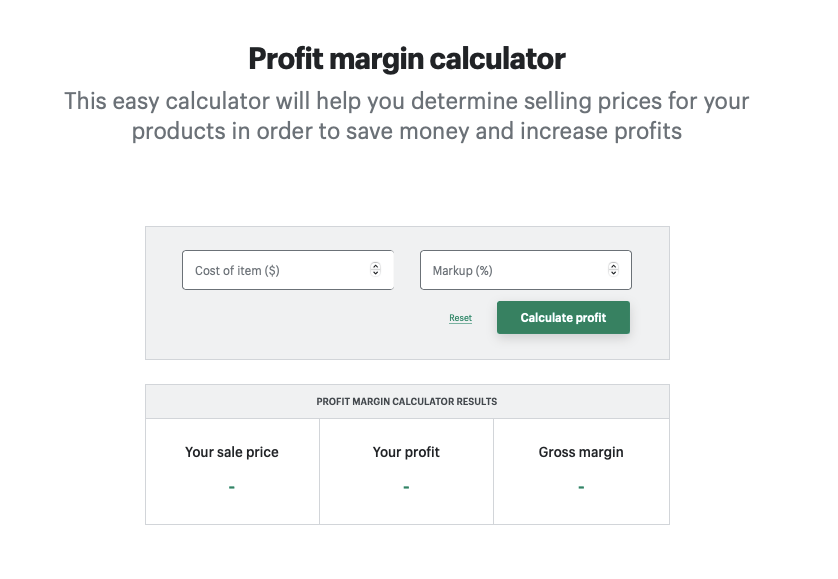
If you want to play around with your own numbers, try using this free profit margin calculator .
To sum up…
Now that you know how to price a product, you’re ready to set your prices and start selling your products to turn a profit! It’s worth noting that there are other pricing strategies that you can use besides the cost-pricing strategy, such as psychological pricing, which is based on the theory that people read from left to right and are therefore more likely to focus on the digits on the left than the ones on the right. As a result, customers subconsciously round prices like $5.99 down to just $5, essentially ignoring the remaining 99 cents. Interesting stuff, right? Shopify has a great guide on different pricing strategies if you want to do some further reading.
Looking to start your own print on demand business or switch dropshipping suppliers? Integrate your store via our Online order form, Shopify App, Etsy Dropshipping and Print API solutions.